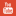
Psoriasis is a most comman disease related to skin.Psoriasis is a chronic , non-contagious autoimmune disease which affects the skin and joints. It causes red scaly patches to appear on the skin. The scaly patches caused by psoriasis , called psoriatic patch,are areas of inflammation and excessive skin production.that gives silvery white appearance.
Psoriasis is quite common , affecting around two per cent of the population, although people with very mild symptoms may not be aware they have it. Psoriasis can begin at any age but usually starts either around the age of 20 or between 50 and 60.
The disorder is a chronic recurring condition which varies in severity from minor localized patches to complete body coverage. Fingernails and toenails are frequently affected (psoriatic nail dystrophy) and can be seen as an isolated finding. Psoriasis can also cause inflammation of the joints, which is known as psoriatic arthritis. In contrast to eczema, psoriasis is more likely to be found on the extensor aspect of the joint.
The cause of the psoriasis is still unclear.
Factor which trigger the psiriasis are
- Heredity – If one parent is affected then there is 15% of chances for the child to suffer from psoriasis. If both the parents are affected then the possibility of child getting the psoriasis is 60%.
- Throat infections trigger psoriasis.
- Trauma or hurt on skin like cuts, bruises or burns may cause psoriasis.
- Some medicines or skin irritants initiate psoriasis.
- Smoking and alcohol are other two factors which activate psoriasis.
- Mental stress or psychological trauma may also set off psoriasis.
- Due to abnormality in the mechanism in which the skin grows and replaces itself
Causes Psoriasis.
- Abnormality with the metabolism of amino acids.
- Use of certain medicines.
- Due to infections.
- Heredity factors are also responsible.
- Physical and emotional stress.
- Diet- common in non-vegetarians
Type Of Psoriasis
- plaque psoriasis
- flexural psoriasis
- Guttate psoriasis
- Pustular psoriasis
- Psoriasis of a fingernail
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Erythrodermic psoriasis
- Non pustular psoriasis
- Drug induced psoriasis
Clinical Features (Symptoms)
- Start as dry, well defined erythematous papules.
- Symmetrical distribution.
- Coin shaped (nummular psoriasis).
- Layers of silvery scales form.
- Papules increase peripherally and coalesce (psoriasis gyrate).
- Become thicker (due to accumulation of scales) to form plaques.
- Candle-grease sign positive: – when psoriatic lesion is scratched, candle grease like scale is produced even from non-scaling lesions.
- Scales looser towards periphery of patch, firmly adherent at centre.
- Auspitz sign positive: – complete removal of scale produces pin-point bleeding.
- Koebner phenomenon positive in acute phase: – psoriatic lesions appear at site of scratching or trauma.
- When patches reach a diameter of 5 cm: – central clearing occurs producing ringed lesions (annular psoriasis).
- Lesions heal with faint staining which disappears slowly.
Complication
- Psoriatic arthropathy
- Exfoliatic dermititis
- Hypoprotienamia
Homeopathy having a most effective solution for psoriasis.